NORMAL
Updated: 31 July 2010
Use NORMAL to calculate the probability density function for the standard normal distribution.
The probability density function of the standard normal distribution is:
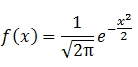
Syntax
SELECT [wctStatistics].[wct].[NORMAL] (
<@X, float,>)
Arguments
@X
is any real number. @X is an expression of type float or of a type that implicitly converts to float.
Return Types
float
Examples
SELECT wct.NORMAL(1)
This produces the following result
----------------------
0.241970724519143
(1 row(s) affected)
SELECT wct.NORMAL(-1)
This produces the following result
----------------------
0.241970724519143
(1 row(s) affected)
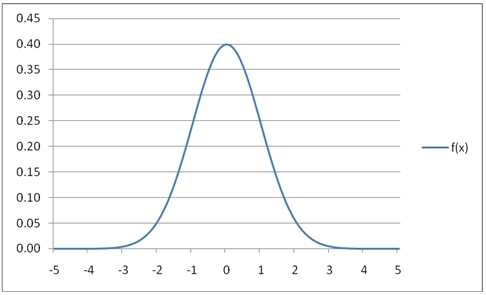
You can use the SeriesFloat function from the XLeratorDB/math library to generate a dataset which can be pasted into EXCEL to generate a graph of the function.
SELECT SeriesValue
,wct.NORMAL(SeriesValue) as [f(x)]
FROM wctMath.wct.SeriesFloat(-5, 5, .1,NULL,NULL)
This is an EXCEL-generated graph of the results:
See Also