Updated: 21 July 2017
Use the SQL Server scalar function STIRLING1 to calculate the Stirling numbers of the first kind. The Stirling numbers of the first kind are the coefficients in the expansion:
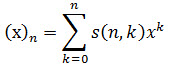
Where (x)n is the falling factorial (see FACTORIALPOWER).
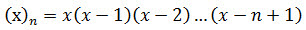
Stirling numbers of the first kind exhibit the following recursive relationship.
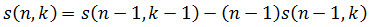
Syntax
SELECT [wct].[STIRLING1] (
<@n, int,>
,<@k, int,>)
Arguments
| Input Name | Definition |
| @n | Number of items |
| @k | Number chosen |
Return Type
Remarks
- If @n <= 0 then NULL is returned.
- If @k < 0 then NULL is returned.
- If @k > n then NULL is returned.
- s(0,0) = 1
- s(n,0) = 0
- Available in XLeratorDB / statistics 2008 only
Examples
Example #1
Calculate the coefficients for the expansion of: x(x-1)(x-2)(x-3)(x-4)
SELECT
wct.STIRLING1(4,1) as [x]
,wct.STIRLING1(4,2) as [x^2]
,wct.STIRLING1(4,3) as [x^3]
,wct.STIRLING1(4,4) as [x^4]
This produces the following result.
The expanded equation would thus be: x4-6x3+11x2-6x
Example #2
A lower triangular representation of the first few Stirling numbers of the first kind.
SELECT [1],[2],[3],[4],[5],[6],[7],[8],[9],[10]
FROM (
SELECT
n.SeriesValue as n
,k.seriesValue as k
,cast(wct.STIRLING1(n.SeriesValue,k.SeriesValue) as int) as S1
FROM
wct.SeriesInt(1,10,NULL,NULL,NULL)n
CROSS APPLY
wct.SeriesInt(1,n.seriesvalue,NULL,NULL,NULL)k
)d
PIVOT (MAX(S1) FOR k IN ([1],[2],[3],[4],[5],[6],[7],[8],[9],[10]))pvt
ORDER BY
n
This produces the following result.
See Also