Updated: 9 August 2010
Use EXPONDIST to calculate an exponential distribution that is equivalent to the function used in EXCEL. Exponential distributions describe times between events in a Poisson process, i.e. a process in which events occur continuously and independently at a constant average rate.
The equation for the probability density function is:
The equation for the cumulative distribution function is:
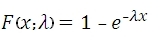
Syntax
SELECT [wctStatistics].[wct].[EXPONDIST] (
<@X, float,>
,<@Lambda, float,>
,<@Cumulative, bit,>)
Arguments
@X
is the value of the function. @X is an expression of type float or of a type that can be implicitly converted to float.
@Lambda
is the parameter value. @Lambda is an expression of type float or of a type that can be implicitly converted to float.
@Cumulative
is a logical value that determines the probability density function (False, 0) or the cumulative distribution function (True, 1) is being calculated.
Return Types
float
Remarks
· If @X < 0, EXPONDIST returns an error.
· If @Lambda ≤ 0, EXPONDIST returns an error
· EXPONDIST = GAMMADIST(@X,1,1/@Lambda, @Cumulative)
· EXPONDIST = WEIBULL(@X,1,1/@Lambda, @Cumulative)
Examples
select wct.EXPONDIST(0.5, 9.5, 'False')
This produces the following result
----------------------
0.082191104429646
(1 row(s) affected)
select wct.GAMMADIST(0.5,1,1.0000000/9.50000000, 'False')
This produces the following result
----------------------
0.0821911044296461
select wct.EXPONDIST(0.5, 9.5, 'True')
This produces the following result
----------------------
0.991348304796879
(1 row(s) affected)
select wct.GAMMADIST(0.5,1,1.0000000/9.50000000, 'True')
This produces the following result
----------------------
0.991348304796879
(1 row(s) affected)