XLeratorDB/math Documentation
HESSIAN
Updated: 15 April 2018
Use the scalar function HESSIAN to numerically compute the Hessian matrix. HESSIAN assumes that the function has continuous partial derivatives. HESSIAN produces a square matrix of second order partial derivatives of a scalar function.
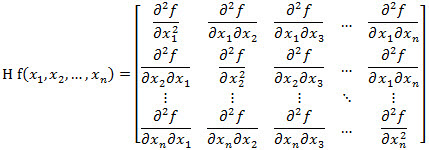
Syntax
SELECT [wct].[HESSIAN] (
<@Func, nvarchar(max),>
,<@VarNames, nvarchar(4000),>
,<@X, nvarchar(4000),>
,<@H, float,>)
Arguments
| Input Name | Description |
| @Func | The function to be evaluated, as a string. The function must be in the form of a SELECT statement. |
| @VarName | The name of the variable |
| @X | The point where the Hessian is calculated |
| @H | Step size |
Return Type
Remarks
- If @Func returns a NULL then NULL Is returned.
- If @Func is not a valid SELECT statement then NULL is returned.
- If no solution is found then NULL is returned.
- If @X is NULL then @X = ''.
- If @H is NULL then @H = 0.
- If @H <= 0 then @H = 2^(-13)
- Available in XLeratorDB / math 2008 only
Examples
Example #1
Calculate the Hessian for the function
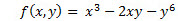
At the point (1,2)
Since the result is returned as a string, we will use the MATRIX function to unpack the results into a matrix format.
SELECT
*
FROM wctMath.wct.MATRIX(
wct.HESSIAN(
'SELECT POWER(@x,3) - 2*@x*@y - POWER(@y,6)'
,'@x,@y'
,'1,2'
,NULL
)
)
This produces the following result.
See Also